Shader
As of 1.12.0, Ebitengine has APIs to render custom shaders. This document explains how to use custom shaders.
What's a shader?
A shader is a program executed on GPU. A custom shader is a shader an Ebitengine user can write. With shaders, you can execute a complex rendering on GPU efficiently.
In Ebitengine, you can write a 'fragment shader'. A fragment shader is a shader executed on each pixel. Roughly speaking, this is a function to calculate a color for each pixel. This color calculation is executed on GPU in parallel.
With shaders, you can execute various effects like lighting or blur. For an example, see examples/shader.
go run github.com/hajimehoshi/ebiten/v2/examples/shader@latestEbitengine adopts an original shading language 'Kage'. This has a compatible syntax with Go, but the details are different. Kage has high portability. Ebitengine uses graphics libraries like OpenGL or Metal and this depends on environments, but Kage is compiled on the fly so that this works equally everywhere.
Example
Ebitengine API
NewShader
func NewShader(src []byte) (*Shader, error)NewShader compiles a shader program in the shading language Kage, and returns the result.
If the compilation fails, NewShader returns an error.
(*Image).DrawRectShader
func DrawRectShader(width, height int, shader *Shader, options *DrawRectShaderOptions)DrawRectShader draws a rectangle with the specified width and height with the specified shader.
DrawRectShaderOptions
DrawRectShaderOptions represents options for DrawRectShader.
type DrawRectShaderOptions struct {
// GeoM is a geometry matrix to draw.
// The default (zero) value is identity, which draws the rectangle at (0, 0).
GeoM GeoM
// CompositeMode is a composite mode to draw.
// The default (zero) value is regular alpha blending.
CompositeMode CompositeMode
// Uniforms is a set of uniform variables for the shader.
// The keys are the names of the uniform variables.
// The values must be float or []float.
// If the uniform variable type is an array, a vector or a matrix,
// you have to specify linearly flattened values as a slice.
// For example, if the uniform variable type is [4]vec4, the number of the slice values will be 16.
Uniforms map[string]interface{}
// Images is a set of the source images.
// All the image must be the same size with the rectangle.
Images [4]*Image
}The others
For more primitive rendering, there are also (*Image).DrawTrianglesShader and DrawTrianglesShaderOptions.
Shading language Kage
Syntax
The syntax is basically same as Go. This is completely same in the syntax level. You can do even gofmt.
Kage doesn't have these Go's features so far.
- Most types (
rune,string, numeric types except forint,interface, slices, pointers, structs, function types, channels) - Built-in functions except for some functions like
len(e.g.,new,make,panic) - New type definition with
type - Structs
importswitchgotofor-range- Goroutines
deferinitfunctions- Method definition
Unit mode
The unit mode was added to Kage as of v2.6. These comments work as compiler directives to specify the unit mode.
//kage:unit texels(Texel mode, default)//kage:unit pixels(Pixel mode)
In pixel mode, all units handled by the Kage shader become pixels.
By default, it is set to texel mode for backward compatibility. For new Kage programs, it is strongly recommended to use pixel mode.
Entry point
Kage can define only a fragment shader. The Fragment function with one of the following signatures is the entrypoint.
func Fragment() vec4func Fragment(dstPos vec4) vec4func Fragment(dstPos vec4, srcPos vec2) vec4func Fragment(dstPos vec4, srcPos vec2, color vec4) vec4func Fragment(dstPos vec4, srcPos vec2, color vec4, custom vec4) vec4
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
dstPos | vec4 | The destination position in pixels. The 3rd and 4th components are always 0 and 1. |
srcPos | vec2 | The source texture's position in texels or pixels. The unit depends on the unit mode. |
color | vec4 | Supplemental color information given from vertices. Each component values are in between 0 and 1. This value is specified by DrawRectShaderOptions.ColorScale or vertices information for DrawTrianglesShader. |
custom | vec4 | Custom values for any purposes. |
| (Returning value) | vec4 | The current position's color. Each component values are in between 0 and 1. |
Built-in types
Kage has these built-in types.
boolintfloatvec2,vec3,vec4(Vector offloats)ivec2,ivec3,ivec4(Vector ofints)mat2,mat3,mat4(Matrix)
float is a floating point number. Unlike Go's float32 and float64, float doesn't have a guarantee for the precision.
vec2, vec3, vec4, called vectors, are tuples that has 2, 3, and 4 components respectively. Each component is float. Swizzling operation is available on vector values.
ivec2, ivec3, ivec4 are also vectors and each component is int.
mat2, mat3, mat4 are 2, 3 and 4 dimensional square matrices. Each component is float. Like GLSL, they use column-major order.
Kage also supports arrays. Kage doesn't support structs yet.
Initializing functions for built-in types
Similar to Go, you can get the type's value by using the type name as a function. Vector types and matrix types are so special that they can take flexible arguments.
v1 := vec4(0) // Returns a vec4 whose components are all 0.
v2 := vec4(1, 2, 3, 4) // Returns a vec4 whose components are 1, 2, 3 and 4.
v3 := vec3(5, 6, 7)
v4 := vec4(1, v3) // Returns a vec4 whose components are 1, 5, 6 and 7.
m1 := mat4(2) // Returns a mat4 whose diagonal components are 2 and the others are 0.
m2 := mat4(v1, v2, v3, v1) // Returns a mat4 whose columns are v1, v2, v3 and v1.Swizzling
There is a special operation called Swizzling for vector types. You can read and write multiple components at the same time.
v1 := vec4(1, 2, 3, 4)
v2 := v1.xyz // Get vec3(1, 2, 3) and initialize v2 with this.
v2.xyz = v2.xxx // Get vec3(1, 1, 1), and set it to all the components to v2.
// Then, v2 is now (1, 1, 1).Each component is represent like below. You can mix them in the same group, but you cannot in different groups. For example, .xxyy and .abgr are available, but .xxgg is invalid.
x,y,z,wr,g,b,as,t,p,q
Uniform variables
A uniform variable is a global variable whose value is given externally. This value is the same regardless of the position of the pixel.
In Kage, uniform variables are global variables that start with upper cases (i.e., exported variables).
You cannot assign a value into a uniform variable in Kage.
You cannot define other global variables than uniform variables in Kage.
Built-in functions (Go)
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
cap(x T) int | T is an array type. Returns the length of the array. (v2.1.0) |
len(x T) int | T is an array type. Returns the length of the array. |
Built-in functions (Control)
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
discard() | Stop outputting the current fragment. (v2.4.0) |
Built-in functions (mathematics)
Most of the built-in functions are generic. T represents float, vec2, vec3 or vec4 unless otherwise noted. When the type is a vector, the function is applied for each component.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
sin(x T) T | Returns \sin{x} |
cos(x T) T | Returns \cos{x} |
tan(x T) T | Returns \tan{x} |
asin(x T) T | Returns \arcsin{x} |
acos(x T) T | Returns \arccos{x} |
atan(y_over_x T) T | Returns \arctan(\mathit{y\_over\_x}) |
atan2(y, x T) T | Returns \arctan(y/x) |
pow(x, y T) T | Returns x^y |
exp(x T) T | Returns e^{x} |
log(x T) T | Returns \log_e{x} |
exp2(x T) T | Returns 2^{x} |
log2(x T) T | Returns \log_2{x} |
sqrt(x T) T | Returns \sqrt{x} |
inversesqrt(x T) T | Returns 1/\sqrt{x} |
abs(x T) T | Returns x if x \ge 0, or -x otherwise |
sign(x T) T | Returns 1 if x \gt 0, 0 if x = 0, or -1 otherwise |
floor(x T) T | Returns a value equal to the nearest integer that is less than or equal to x |
ceil(x T) T | Returns a value equal to the nearest integer that is greater than or equal to x |
fract(x T) T | Returns x - \mathrm{floor}(x) |
mod(x, y T) T | Returns x - y \cdot \mathrm{floor}(x/y) |
min(args ...T) T | Returns the minimum value of \mathrm{args}. Up to Ebitengine v2.8, the number of arguments was limited to 2. |
max(args ...T) T | Returns the maximum value of \mathrm{args}. Up to Ebitengine v2.8, the number of arguments was limited to 2. |
clamp(x, min_value, max_value T) T | Returns \min(\max(x, \mathit{min\_value}), \mathit{max\_value}) |
mix(x, y, a T) T | Returns x \cdot (1 - a) + y \cdot a |
step(edge, x T) T | Returns 0 if x \lt \mathit{edge}, or 1 otherwise |
smoothstep(edge0, edge1, x T) T | Returns 0 if x \le \mathit{edge0}, 1 if x \ge \mathit{edge1}, or performs smooth Hermite interpolation between 0 and 1 otherwise |
length(x T) float | Returns \sqrt{x[0]^2 + x[1]^2 + \cdots} |
distance(p0, p1 T) float | Returns \mathrm{length}(p0 - p1) |
dot(x, y T) float | Returns x[0] \cdot y[0] + x[1] \cdot y[1] + \cdots |
cross(x, y vec3) vec3 | Returns x \times y (cross product) |
normalize(x T) T | Returns a vector in the same direction as x but with a length of 1 |
faceforward(n, i, nref T) T | Returns n if \mathrm{dot}(\mathit{nref}, i) \lt 0, or -n otherwise |
reflect(i, n T) T | Returns i - 2 \cdot \mathrm{dot}(n, i) \cdot n |
refract(i, n T, eta float) T | (v2.4.0) |
transpose(m T) T | T is a matrix type. Returns a matrix that is the transpose of x |
dfdx(p T) T | (Note that this function's results depend on internal states and are indeterministic) |
dfdy(p T) T | (Note that this function's results depend on internal states and are indeterministic) |
fwidth(p T) T | (Note that this function's results depend on internal states and are indeterministic) |
frontfacing() bool | Returns whether the current fragment is front-facing or not. (v2.9.0) |
Built-in functions (images)
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
imageSrcNAt(pos vec2) vec4 | Returns the color value as vec4 at the given position pos of the source image N in texels or pixels . The unit depends on the unit mode. N is 0 to 3. pos is always a position of 0th texture, whichever N is. For N ≧ 1, Kage automatically converts the given position to an appropriate position of the N-th texture. |
imageSrcNUnsafeAt(pos vec2) vec4 | Returns the color value as vec4 at the given position pos of the source image N in texels or pixels . The unit depends on the unit mode. N is 0 to 3. pos is always a position of 0th texture, whichever N is. For N ≧ 1, Kage automatically converts the given position to an appropriate position of the N-th texture.The difference from the safe version ( imageSrcNAt) is the returning value when the position is out of the bounds. The safe version returns vec4(0) in this case, while the unsafe version's returning value is undefined. The unsafe version is faster. If you are sure that the position is in the bounds, you can use the unsafe version for performance. |
imageSrcNOrigin() vec2 | Returns the upper-left position of the source image N in texels or pixels on the texture. The unit depends on the unit mode. |
imageSrcNSize() vec2 | Returns the size of the source image N in texels or pixels on the texture. The unit depends on the unit mode. |
imageDstOrigin() vec2 | Returns the upper-left position of the destination image in texels or pixels on the texture. The unit depends on the unit mode. |
imageDstSize() vec2 | Returns the size of the destination image in texels or pixels on the texture. The unit depends on the unit mode. |
These functions are deprecated as of the version 2.6.
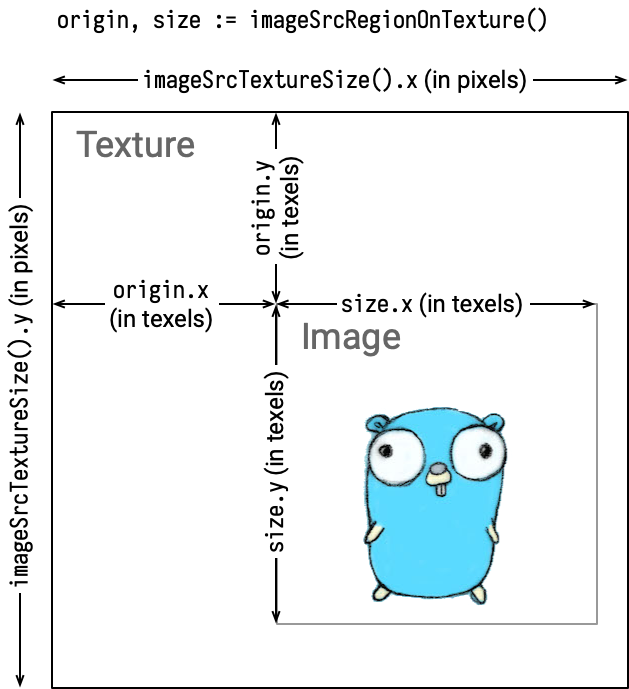
imageSrcTextureSize() vec2 | Returns the source image's texture size in pixels |
|---|---|
imageDstTextureSize() vec2 | Returns the destination image's texture size in pixels |
imageSrcRegionOnTexture() (vec2, vec2) | Returns the source image's origin position and the size on the texture in texels or pixels. The unit depends on the unit mode. |
imageDstRegionOnTexture() (vec2, vec2) | Returns the destination image's origin position and the size on the texture in texels or pixels. The unit depends on the unit mode (v2.1.0) |
Textures and images
Ebitengine's image (ebiten.Image) is actually a part of an internal texture.
In pixel mode, all units are in pixels, so there's not much to be particularly aware of. On the other hand, in texel mode, the coordinate calculations on the shader become a bit more complex. The following explanation is mainly for when using texel mode.
A pixel is a unit for one color dot. On the other hand, texel is a unit covering the whole area with values in between 0 and 1. The meaning of texels depends on a texture, then you cannot mix texels with different textures.
To convert pixels and texels each other, you can use these formulas.
\begin{aligned} (\text{texels}) &= \frac{(\text{pixels})}{(\text{the texture's size in pixels})} \\ (\text{pixels}) &= (\text{texels}) \cdot (\text{the texture's size in pixels}) \\ \end{aligned}
Tutorials
Editor Plugins
There are plugins for some editors by volunteers to edit Kage programs.